top of page
01
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate, PC
Polycarbonate is a colorless and transparent amorphous thermoplastic. Its name is derived from the containing CO3 group.
Characteristics
-
Polycarbonate is colorless, transparent, heat resistant, impact resistant, flame retardant, and has good mechanical properties under normal operation temperature. Compared with polymethyl methacrylate with similar properties, polycarbonate has better impact resistance, high refractive index, and good processability. It can reach the UL94 V-0 flame-retarding performance without any additives. However, polymethyl methacrylate is relatively cheap and can produce large devices by bulk polymerization. Nowadays, with the increasing production of polycarbonate, the price difference between polycarbonate and polymethyl methacrylate is decreasing.
-
Polycarbonate will release pyrolysis gas when it burns. The plastic will burn, but it will not ignite. The burning will be stopped when the material is kept away from the fire source. When burning, polycarbonate will release a light phenol smell and the flame will be yellow, emitting a pale black-color light. Polycarbonate will begin to soften when the temperature reaches 140°C, and melt when the temperature reaches 220°C. Polycarbonate can absorb light in the infrared spectrum.
-
Polycarbonate has poor wear resistance. Some polycarbonate devices used for wear and tear applications require special surface treatment.



1/1
Applications
-
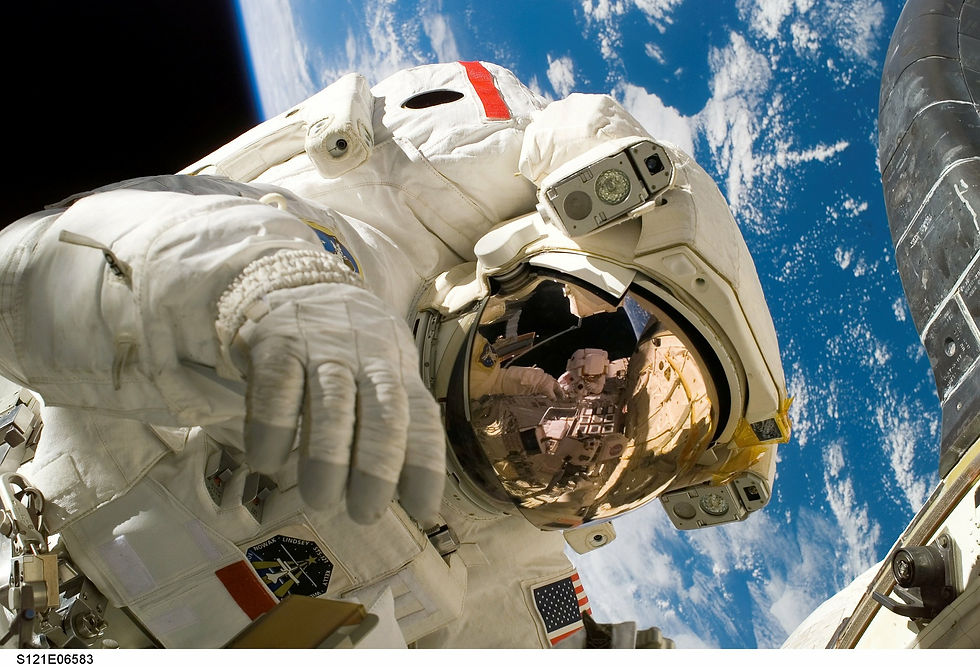
CD/VCD disc, water bottle, baby bottle, resin lens, bulletproof glass, headlight cover, animal cage, suitcase, space helmet mask for astronaut and protection case for smart phones.
02
ABS Resin (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene copolymer)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Characteristics
-
ABS is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good stiffness and processability. Its glass transition temperature is about 105°C (221°F). ABS resin is a milky white solid with certain stiffness and density of about 1.04~1.06 g/cm3. It has strong resistance to acid, alkali and salt, and can also tolerate the dissolution of organic solvent to some extent.

1/1
Applications
-
ABS resin can operate normally under the temperature of -25°C ~ 60°C, and has good formability. The surface of the processed product is smooth, allowing for the ease of dyeing and electroplating.
-
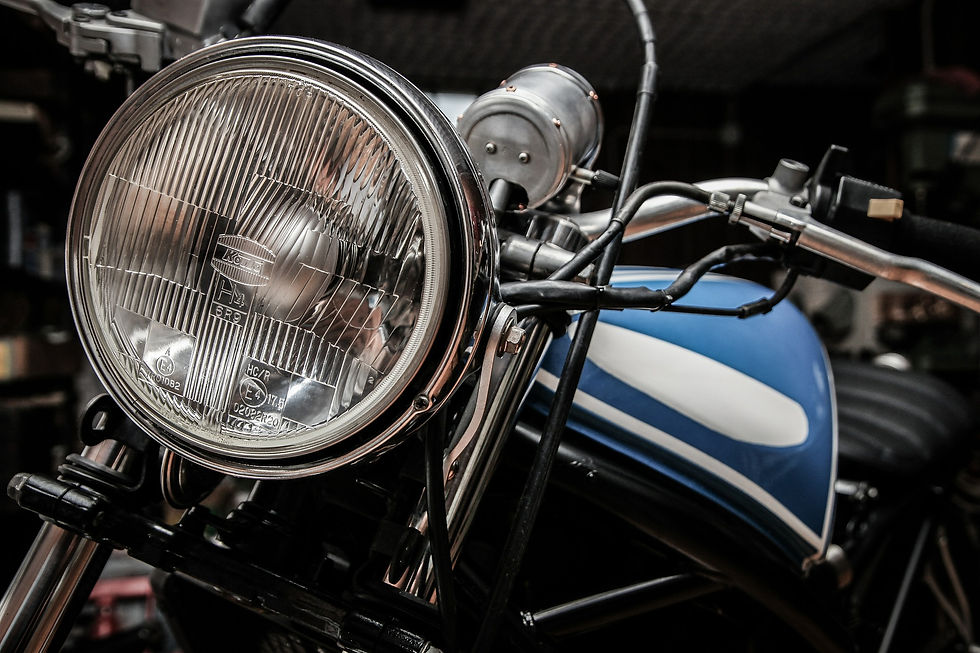
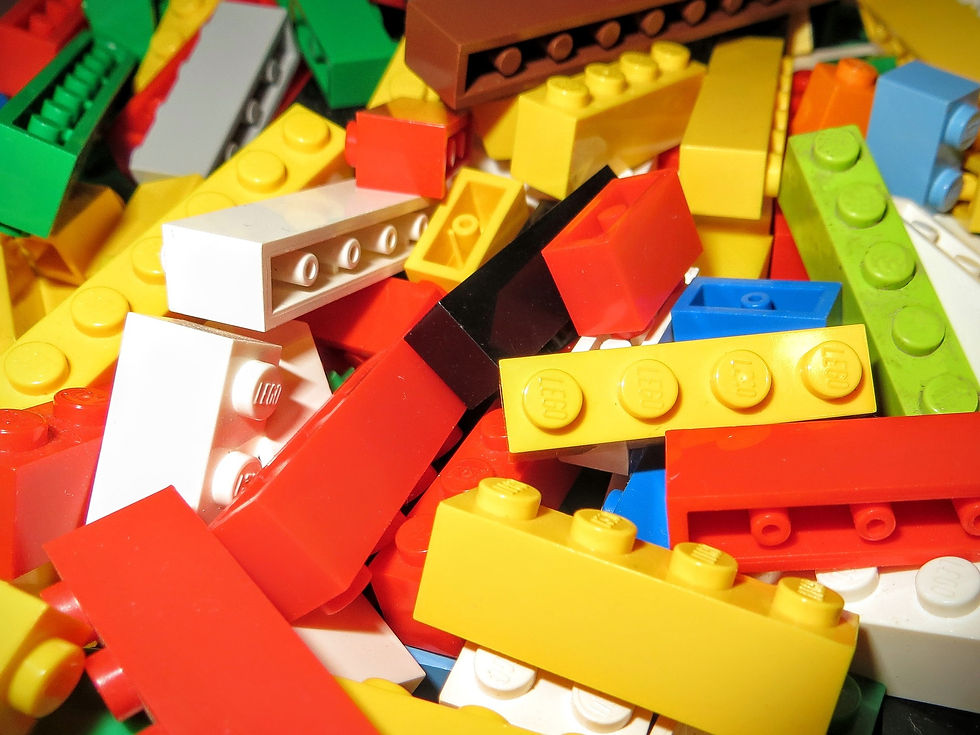
ABS resin can be used for household appliances, toys and other daily necessities. The well-known Lego bricks are made of ABS resin.
03
Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic. It has high impact resistance, good mechanical strength, and strong resistance to corrosion against various organic solvents, acids and bases.
Characteristics
-
The structure of polypropylene is close to that of polyethylene; therefore, it has several properties that are similar to those of polyethylene, especially the reactivity and electrical properties in solution. Due to the presence of a methyl side chain, polypropylene has improved mechanical properties and heat resistance. However, it is more susceptible to oxidative degradation comparing with polyethylene under the action of ultraviolet light and heat, resulting in reduced chemical resistance.
-
Polypropylene has good heat resistance and chemical stability. Intrinsically, it is similar to high-density polyethylene, with crystallinity slightly lower than that of high-density polyethylene. As a result, polypropylene is typically translucent and has hardness similar to that of high-density polyethylene. The properties of polypropylene depend on factors such as molecular weight, molecular weight distribution, crystallinity, and type/ratio of comonomer (if used), etc.
Applications
-
The melting point of PP is as high as 167°C. It is heat resistant, and its products can be steam sterilized.
Bottles made of PP include soy milk, rice milk bottles, and bottles for 100% pure juice, yogurt, juice, beverage, dairy products (such as pudding), etc.
-
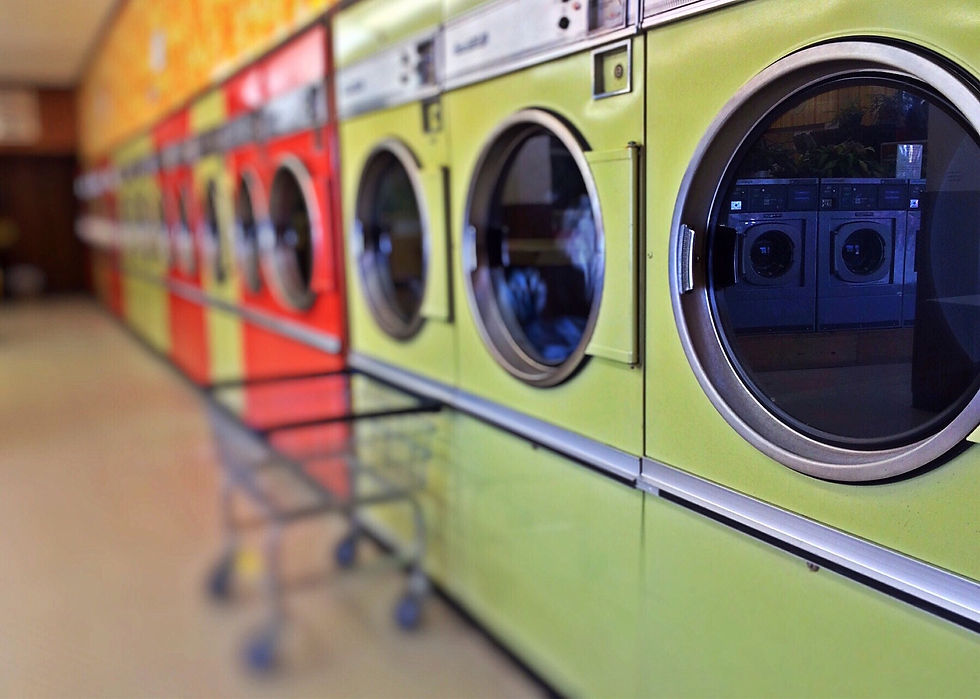
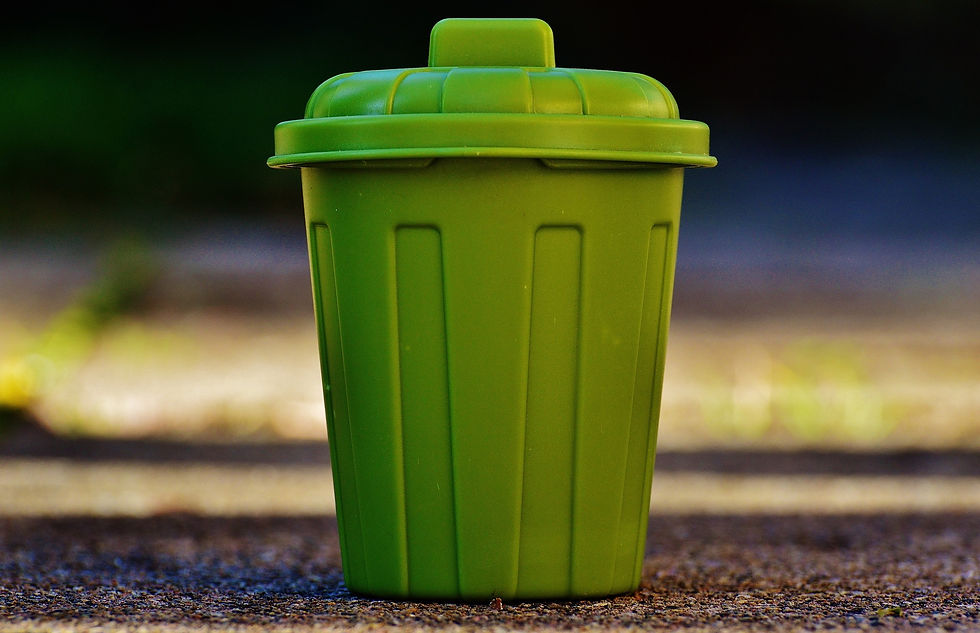
Large containers, such as buckets, trash cans, laundry tanks, baskets, etc. are mostly made of PP.
-
In recent years, PP has also been widely used in disposable tableware or disposable cups (used as iced beverage containers by many fast food & beverage shops, such as the containers used by the famous franchise "Quickly" in the market)
-
The container made of PP is opaque or translucent, and has several advantages such as acid/base resistance, chemical resistance, impact resistance and high temperature resistance (about -20°C ~ 120°C).




1/1
04
Tempered plastics
Tempered plastics exhibit strength and rigidity when they are static or subjected to low-speed impact. They exhibit ductility and energy absorption property when subjected to high-speed impact, and are less prone to brittle failure. Typical tempered plastics include PC/ABS, PC/SAN, PC/PBT, PC/PP, and PC/PMMA.
Characteristics
-
When tempered plastic is static or subjected to low-speed impact, it demonstrates the strength and rigidity in ordinary engineering plastics. On the contrary, when it is subjected to high-speed impact, it exhibits rubber-like ductility and toughness, thereby, functioning as energy absorption and protection material. As for the ordinary toughened plastic, when it is subjected to high-speed impact, large number of cracks will begin to form and expand, resulting in brittle fracture.
-
Even if the material is damaged by external force, the damaged area will show toughness fracture, rather than brittle fracture such as the formation of sharp corners and the splattering of fragments.
-
Special stress-strain behavior: As the tensile speed increases, the tensile modulus of ordinary engineering plastic alloys increases, while the elongation at break decreases. Conversely, as the tensile speed of "tempered plastics", increases, the tensile modulus is reduced while maintaining a high elongation at break.
-
Tempered plastic has high energy absorption under high-speed impact: ordinary engineering plastic alloys are often characterized by rigid and brittle fracture when subjected to high-speed impact, and are prone to crack propagation; while "tempered plastics" exhibit energy absorption and toughness fracture, which can suppress the formation of cracks, sharp corners and fragments.




1/1
Applications
-
Tempered plastic can be applied to automotive interior and exterior parts and plays an important role in collision protection and energy absorption to improve the safety of automobiles.
-
Tempered plastic can be applied to sports equipment. When joints are subjected to impact, the impact force can be quickly absorbed to better protect the body skeleton.
05
Polyethylene
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is one of the most commonly used polymer materials in everyday life. It is widely used in the manufacturing of plastic bags, plastic films, and milk barrels.
Characteristics
-
Polyethylene can be considered as transparent in the form of film; however, in bulk, due to the presence of large amount of crystals within the material, strong light scattering occurs which makes it opaque. The degree of crystallization of polyethylene is affected by the number of its branches, and the more the branches, the more difficult it is to crystallize. The crystal melting temperature of polyethylene is also affected by the number of its branches. The crystal melting temperature ranges from 90°C to 130°C, and the more the branches, the lower the melting temperature. Polyethylene single crystals can usually be prepared by dissolving high-density polyethylene in xylene at temperature above 130°C.


1/1
Applications
(1).High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
-
High-density polyethylene has good structural strength and impact resistance. It is opaque and often used as the container for dairy products. This type of plastic is resistant to water and oil; therefore, it has wide applications. Generally, high-density polyethylene will start to deform when the temperature reaches above 100°C. Furthermore, high-density polyethylene is also resistant to corrosion from acids and bases; therefore, it has been widely applied in the industry.
(2).Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
-
The density of low-density polyethylene is lower comparing with that of high-density polyethylene. Its structure is shown in the figure below. Low-density polyethylene is very soft and somewhat sticky. Since LDPE has low crystallinity, its transparency is relatively high; therefore, it is mainly used for making products such as plastic wrap and plastic bags, etc. Moreover, LDPE has relatively low oil resistance and water resistance comparing with HDPE.
06
Polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene Terephthalate
(PET or PETE)
Polyethylene terephthalate is a resin commonly seen in everyday life and can be divided into APET, RPET and PETG.
Characteristics
-
Polyethylene terephthalate is a thermoplastic polyester with excellent toughness, tensile strength, impact strength, abrasion resistance and electrical insulation.
-
Since PET has characteristics such as good toughness, air-tightness, light weight, acid/base resistance, water resistance and oil resistance, it has become a common packaging container for soda, juice, carbonated beverages, edible oil, etc., in recent years.
-
Shrinkage rate of 70%
-
Polyethylene terephthalate is not heat resistant. It is free from deformation at temperature below 80°C.
Applications
-
The molecular weight of polyethylene terephthalate is large enough to be spun into polyester fiber, and the finished product is called polyester, which is the basic raw material for various industrial products.
-
Polyethylene terephthalate can be used as the basic material for making music tapes, video tapes, movie films, optical discs, insulation films, packaging materials, etc.
-
As a plastic material, PET can be blown into various kinds of bottles, such as PET bottles.
-
PET can be used for making electrical components, bearings, gears, etc.
-
Most of the recycled beverage bottles have been used for making the plastic ropes.
-
PET can also be used for making polarizer, optical products and liquid crystal displays (LCDs).
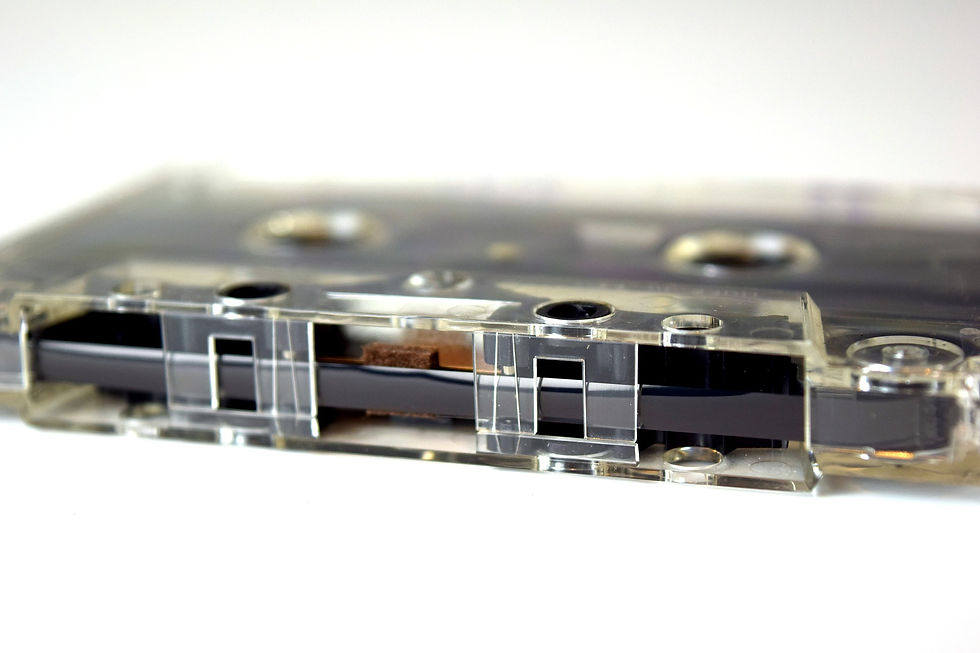
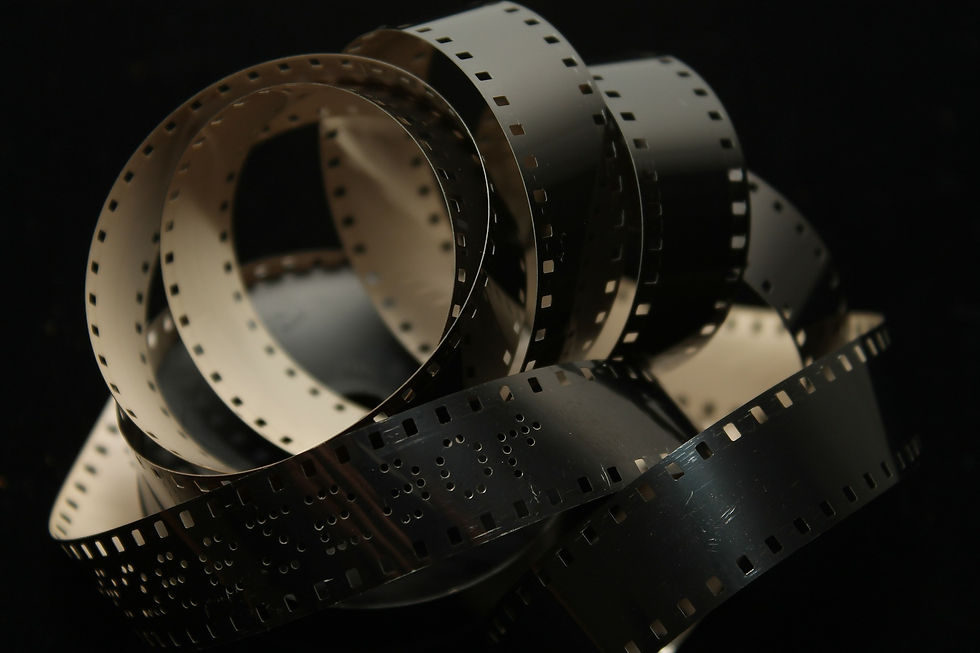



1/1
07
Polyvinyl chloride
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride is a polymer material obtained by addition polymerization of vinyl chloride. It is the third most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer after polyethylene and polypropylene.
Characteristics
(1).lame retardant
-
The biggest advantage of polyvinyl chloride is flame retardant and is therefore widely used in fire protection applications.
-
The burning of PVC is divided into two steps. First, hydrogen chloride gas and a double bond-containing diene are released during the combustion of polyvinyl chloride at 240°C to 340°C, and then carbon combustion occurs at 400 to 470°C.
(2).Stable
-
PVC is not easily corroded by acids or bases. It is a better heat resistant than polyethylene but not as good as polypropylene. PVC is the only material in the seven types of plastics that requires plasticizer, which allows its texture to change from soft and elastic to hard and brittle. Plasticizer is the notorious "additive" that has been widely reported in the news recently. Since PVC can be turned into a soft and elastic material, it can act as rubber or leather and can be applied in making products such as car-interior artificial leather, disposable gloves, floor, tablecloth, and plastic shoes.




1/1
Applications
-
Polyvinyl chloride can be prepared by the substitution reaction of ethylene, chlorine and catalyst. Due to its fire and heat resistance, PVC is widely used in a wide range of products for various applications: cable sheaths, optical fiber sheaths, shoes, handbags, bags, accessories, signs and billboards, architectural and decorative items, furniture, ornaments, rollers, pipes, toys (such as the famous "Rody" from Italy), anime dolls, curtains, roll-up doors, auxiliary medical supplies, gloves, plastic wrap for certain foods, certain clothing, etc.
08
Polyformaldehyde (or polyacetal), also known as polyoxymethylene
Polyformaldehyde (POM)
Polyformaldehyde is a thermoplastic crystalline polymer.
Characteristics
-
Polyformaldehyde is easily crystallized and has a crystallinity of 70%. Its crystallinity can be increased by high-temperature annealing. The homo-polyformaldehyde has a melting temperature of 181°C and a density of 1.425 g/cm3. The melting point of the co-polyformaldehyde is about 170°C. The glass transition temperature of homo-polyformaldehyde is -60°C. Phenolic compounds are the best solvents for polyformaldehyde. From the study of the Melt Flow Index (MI), it is known that the molecular weight distribution of homo-polyformaldehyde is small. Except strong acids, oxidizing agents and phenol, co-polyformaldehyde is stable against other chemical agents. In addition to the abovementioned chemicals, homo-polyformaldehyde is also unstable in concentrated ammonia. The stabilized polyformaldehyde can be heated to 230°C without showing significant decomposition. Polyformaldehyde can be formed by hot pressing, injection, extrusion, blow molding, etc., and the processing temperature is 170-200°C. It can also be processed by machine tools and welding. The products of polyformaldehyde are lightweight, hard, rigid, elastic, structurally stable, low in coefficient of friction, low in water absorption, good in insulation and organic solvent resistant. It can be used in a wide temperature range (-50 ~ 105°C) and humidity range. Its performance can be maintained under the action of various solvents and chemical agents, as well as under heavy load and long-term stress.


1/1
Applications
-
Polyformaldehyde can be used as engineering plastics to replace color metals such as copper. It can be used in automotive and machinery industries for making products such as gears, pumps, self-lubricating bearings, impellers, extrusion screws, valve stems, nuts, etc., as well as insulating devices. Furthermore, it can be used in making tanks, pipes and pesticide sprayers.
泳鉅鑫再生塑料股份有限公司
Yong Jyu Sin Plastic Co., Ltd.
HEAD OFFICE
No. 752, Hudong Rd., Xinhua Dist., Tainan City 712016, Taiwan
CONTACT US
Email : info@yongsin.tw
Tel : +886-6-5801106
Fax : +886-6-5901188
FOLLOW US
bottom of page

